
Tony Buzan has changed the lives of millions with Mind Maps, his revolutionary system of note-taking that.iPhone. 1.7 Additional PMP® Study Resources (already updated/will be updated for new PMP® Exam in 2021)This book is the definitive guide to Mind Mapping. When you think about it, decomposing processes into ITTO reduces each to its most fundamental and basic components, and does so in a standardized manner that is equally applicable for all processes and projects. ITTO are a standardized means of systematically using the same method of developing and executing processes and projects.
The primary aim of scope management to define the exact scope of work and to prevent scope creep (additional requirements added without any proper control) or gold-plating (added by the project team with a view to impressing stakeholders). Effective Project Management Using Mind Maps. Pmbok 5th Edition Mindmap Scribd. The project manager would need to ensure the inclusion of all and only the work required to complete the project successfully (to achieve project objectives to deliver business values).SpringBOK Training Mind Map for PMP exam prep PDF. This PMP ITTO game will test your knowledge of ITTO which are very important in PMP exam and it enables your 'photographic memory' while you are playing.
Including testing & quality assurance, assessed against the Project Management Plan Project Scope – activities and processes needed to be performed to deliver the product scope, assessed against the scope baseline (scope statement, WBS and WBS dictionary), e.g. WBS includes only the deliverables/outcomes/results (not actions) Scope Baseline: scope statement + WBS + WBS dictionary
Itto Mind Map How To Prevent Scope
includes how to prevent scope creep, how to handle change requests, escalation path for disagreement on scope elements between stakeholders, processes for creating scope statement, WBS, processing CR, how the deliverables will be accepted Scope Management Plan (will form part of the Project Management Plan): how the scope will be defined, validated and controlled Outputs: Scope Management Plan, Requirements Management Plan Tools & Techniques: Expert Judgement, Data Analysis, Meetings Inputs: Project Charter, Project Management Plan, EEF, OPA
Requirement: a condition/capability that must be met /possessed by a deliverable to satisfy a contract/standard/etc., including quantified/documented needs, wants, expectation of the sponsor/stakeholder/customer Outputs: Requirements Documentation, Requirements Traceability Matrix Tools & Techniques: Expert Judgement, Data Gathering, Data Analysis, Decision Making, Data Representation, Interpersonal and Team Skills, Content Diagram, Prototypes Inputs: Project Charter, Project Management Plan, Project Documents, Business Documents, Agreements, EEF, OPA the requirement management plan is the primary means to understand and manage stakeholder expectations includes how to process requirements, address missed requirements, configuration management, prioritize requirements, metrics (and rationale) for defining the product, define the traceability structure (in RTM), authorization level for approving new requirements
Quality requirements : quality criteria defined by stakeholders Project requirements : actions/processes/conditions the project needs to met Transitional requirements : temporary capability including data conversion/tracking/training Solution requirements – functional (product behavior) and nonfunctional requirements (reliability, security, performance, safety, etc.)
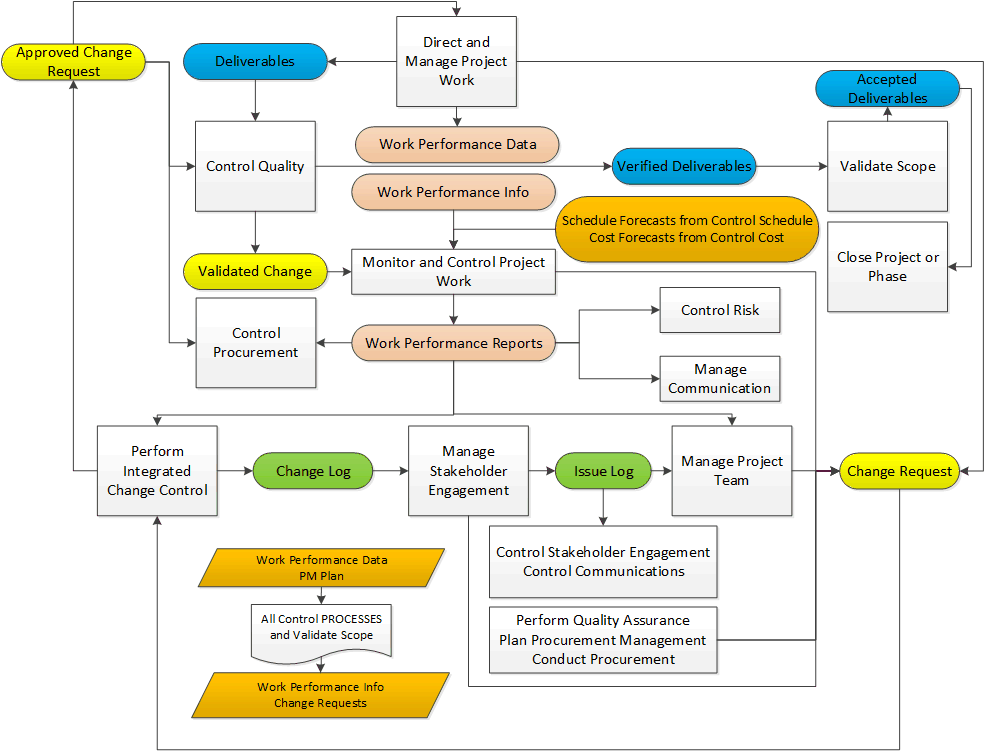
may provide alternatives if the budget and schedule could not meet management’s expectations vs project charter which includes only high-level descriptions to define both the project & product scope in details, outlines what WILL and what WILL NOT be included in the deliverables, including details of constraints and assumptions Outputs: Project Scope Statement, Project Documents Updates Tools & Techniques: Expert Judgement, Data Analysis, Decision Making, Interpersonal and Team Skills, Product Analysis
Tools & Techniques: Expert Judgement, Decomposition Inputs: Project Management Plan, Project Documents, EEF, OPA the scope statement is usually progressively elaborated throughout the project Project Scope Statement includes objectives, (project and product) scope, requirements, boundaries, deliverables, acceptance criteria, constraints, assumptions, milestones, cost estimation, specifications, configuration management requirements, approval requirements, etc. value engineering – a part of product analysis technique (Value Engineering (value analysis, value management, value methodology) with a view to finding alternatives to constraints to improve product/reduce cost without sacrificing the scope)
By phase or major deliverables WBS is a decomposition tool to break down work into lowest level manageable (time and cost can be estimated, work package can be assigned to a team member) work packages, e.g. WBS is a structured hierarchy created by the organization/stakeholders, can be in an organization chart or table form, based on the project deliverables (not tasks needed) the WBS must be created for every project (if you take on a running project without WBS, you must stop the project immediately and prepare the WBS first)
Itto Mind Map Code Of Accounts
code of accounts: a numbering system to identify WBS components a work package can have only ONE control account a higher level above a work package is ‘ control account‘ (control point where scope, cost and schedule are compared to earn value for performance measurement) WBS does not show dependencies between work packages, but a WBS dictionary does (WBS dictionary clarifies WBS by adding additional information) 8 – 80 hours work and different work packages can be at different levels of decompositions
Scope Baseline, an output from Create WBS, includes: the major deliverables should always be defined in terms of how the project will actually be organized, for a project with phases, the decomposition should begin with the phase first 1.1 for the 2nd level, 1.1.1 for the 3rd level
the purpose of this process is to gain formal acceptance of deliverables from customer/ stakeholders (e.g. Outputs: Accepted Deliverables, Work Performance Information, Change Requests, Project Documents Updates Tools & Techniques: Inspection, Decision Making Inputs: Project Management Plan, Project Documents, Verified Deliverables, Work Performance Data
work performance data tells how the deliverables were created, work performance data includes non-conformance and compliance data if no formal sign off is received as stipulated, the Project Manager needs to follow the pre-defined process in PM plan, e.g. change requests may be an output as stakeholders may request changes to the deliverables
need to perform even in case of early termination/cancellation of the project to save any usable deliverables for other projects Unit testing -> high quality vs low quality vs Control Quality: the process of monitoring/recording results of executing quality activities to assess performance and recommend necessary changes, e.g.
the customer has the ultimate authority to change scope while the senior management can make use of management reserves a well documented and enforced change control process is required measure the work product against the scope baseline to ensure the project stays on track proactively, may need preventive, corrective actions or defect repair to prevent unnecessary changes (either internally or externally requested) to the project Control Scope is performed when assessing additional requirements by the customer or the project manager proactively overlooking the project scope Outputs: Work Performance Information, Change Requests, Project Management Plan Updates, Project Documents Updates
variance analysis – method to compare planned (baseline) and actual work and determine the causes/actions e.g.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
